Posts Tagged by charles sable
The Sweetgrass Basket: An African American Tradition
Visitors to the “Lowcountry,” the coastal areas of South Carolina and Georgia — which include the historic cities of Charleston and Savannah — always notice the distinctive stands selling coiled "Gullah" or sweetgrass baskets.
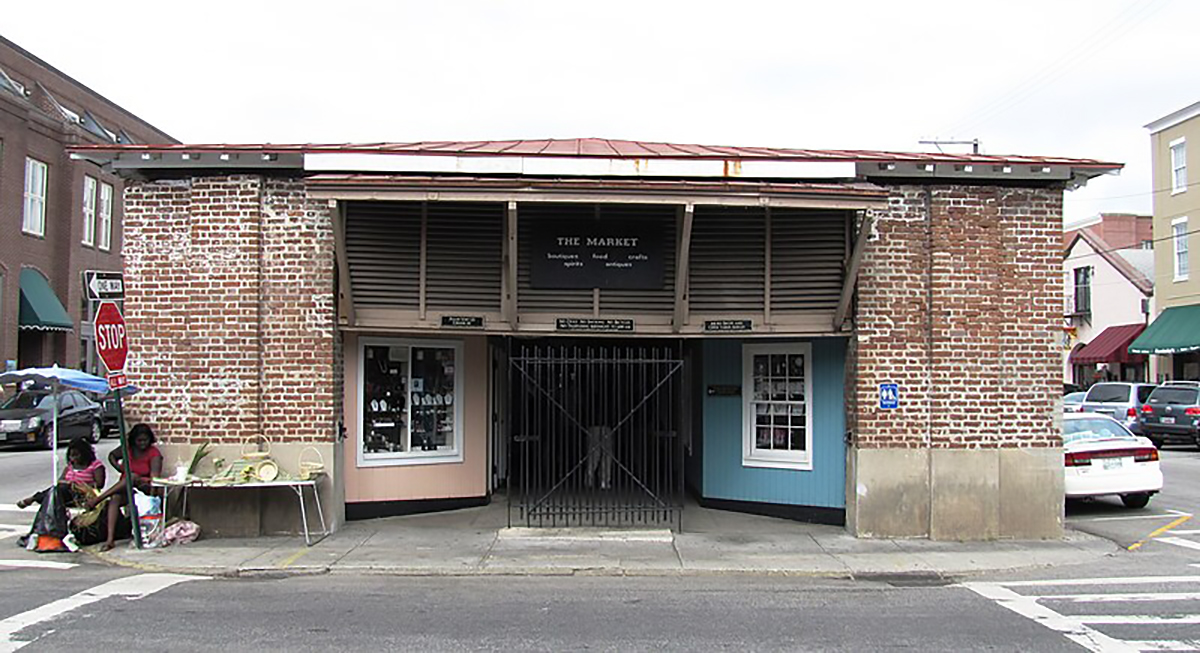

In this image, Gullah sweetgrass basket vendors are visible selling their wares in front of the Old City Market Shed, Charleston, SC, 2010. Photograph by Brian Stansberry.
Throughout Charleston and especially in neighboring Mount Pleasant, vendors line roads selling these homemade crafts, some exquisitely intricate, to locals and visitors alike.
The art of sweetgrass basket weaving is practiced in coastal and barrier island communities from North Carolina to Florida, a region known as the Gullah-Geechee Cultural Heritage Corridor. The Gullah-Geechee people are the descendants of enslaved West Africans who worked on coastal plantations. Because of their isolation, they were able to hold onto many traditions during multiple generations of enslavement in the United States.
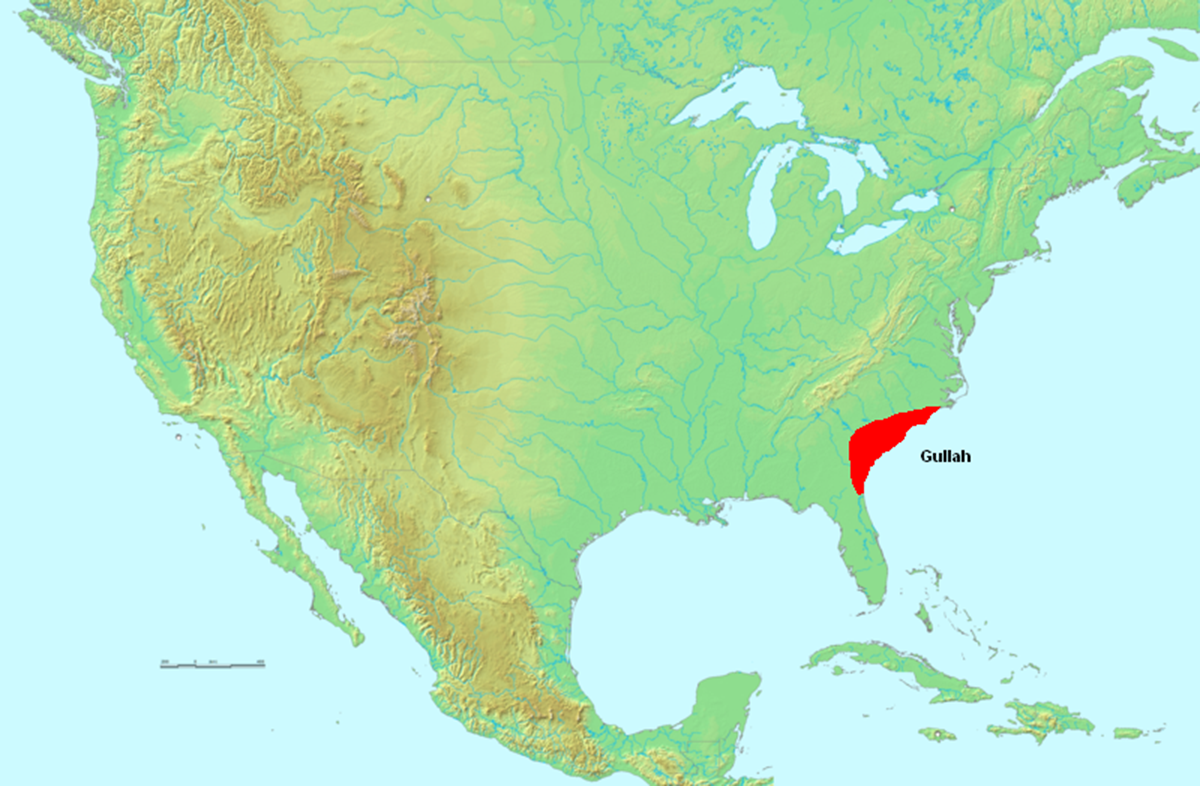
The Gullah region once extended from southeast North Carolina to northeast Florida.
Slave traders abducted African people from the west coast of Africa to the South Carolina Lowcountry beginning in the early 18th century. As part of their work on the rice plantations, enslaved persons made these utilitarian baskets, generally for the storage of dry goods, although some of the baskets were so tightly woven that they could be used to store liquids too. Flat baskets called "fanners" were used in the winnowing of rice. Britannica notes that once the rice was harvested and pounded in a pestle with a mortar, a fanner was used to toss it upward into the wind, which blew away the husk, or chaff.
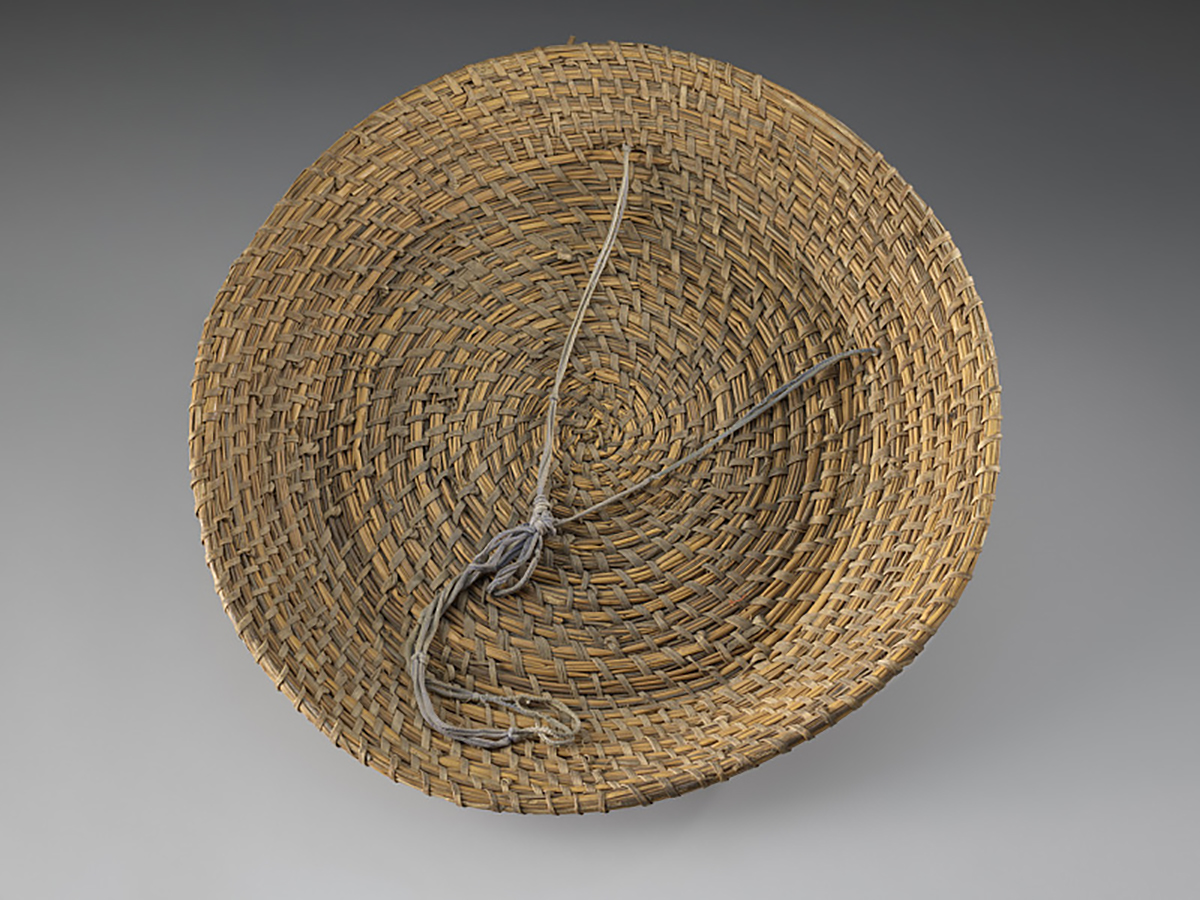

An example of a fanner basket described above, dating to before 1863. From the Collections of the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of African American History and Culture.
According to Britannica, among enslaved persons, “baskets were made by using a sewing technique rather than a plaiting or braiding technique, unlike baskets of European origin. Long ropes of needlegrass rush (Juncus roemerianus; called bulrush, rushel, or needlegrass) were coiled, one on top of the other, and the coils were held together with strips of white oak bark or saw palmetto. Today makers prefer to use sweetgrass with needlegrass rush and longleaf pine needles (Pinus palustris), sewing these with palmetto leaf (Sabal palmetto), and they produce designs without dyes by alternating the natural colors of the dried yellowish green sweetgrass, reddish brown, black needlegrass rush, and green longleaf pine needles. The only tools required for basket production were scissors and 'sewing bones'— filed down teaspoon handles — or 'nail bones' (made from flattened nails or rib bones of a cow or pig). The 'bones' were used to tuck the palmetto around the coils."
In general, men collected the materials that women transformed into baskets. Depending on its size and function, a single basket could take weeks or even months to make according to Britannica. These baskets (which remained the same for more than 300 years) relied on the sharing of traditional knowledge across many generations, as mothers taught their daughters the technique to create them.
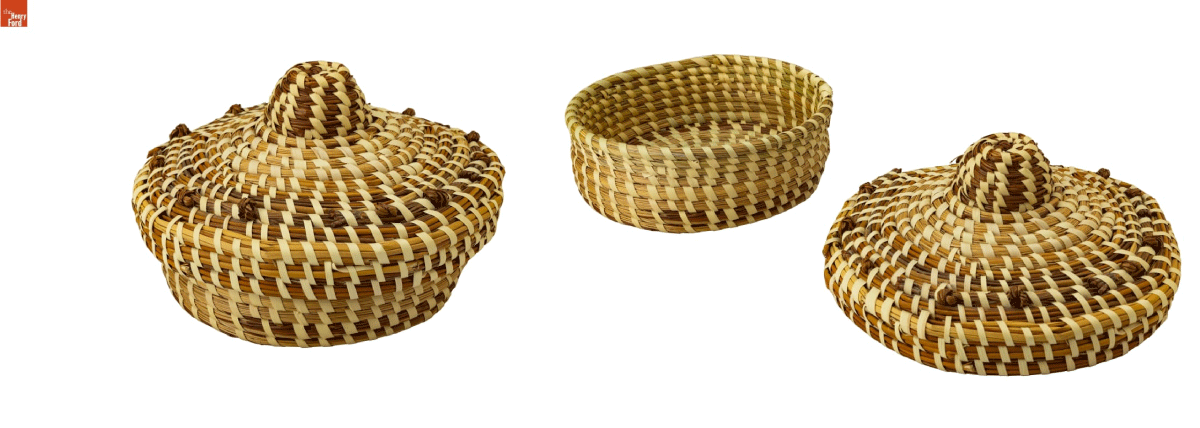

A sweetgrass basket from 2011, made by Carol Lee Howard, born in 1958 in Mount Pleasant, South Carolina. / THF802432 (left), THF802433 (right)
This basket is a typical representation. It recently came into the Henry Ford collection from a donor who acquired it in South Carolina. When it was offered for the collection, all we had was a price tag, with the maker's name and a receipt from 2011. After a bit of sleuthing, we located and contacted the maker, Carol Lee Howard.
Ms. Howard grew up in a family where sweetgrass baskets were a family tradition, spanning generations. She says that her mother, grandmother, and all her aunts and siblings learned how to make these baskets for "extra income." As a young person, she was reluctant to make them until her sister Lillie Howard (who died in 2011) challenged her to make them in the early 1980s. Carol Lee accepted her sister's challenge and now views the making of these baskets as part of her family's heritage.
She said that she became serious about making baskets in the early to mid-1990s, selling them at fairs in Charleston, and through local venues. Today, she spends her time taking care of her grandchildren and occasionally making baskets. This recent acquisition represents Ms. Howard's expertise as a basket maker — and the enduring traditions of resourcefulness and resilience found in American craft movements.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford.
Pattern, Paint, and Peacocks: An Introduction to the Whimsical Art of the Pennsylvania Germans at The Henry Ford

New Year’s Wish for Jacob Grimm and Family, 1784, made by Daniel Schumacher (active 1728-1787), worked in Berks, Lehigh, and Northampton Counties. 61.148.1 / THF237518
The Pennsylvania Germans, popularly known as the Pennsylvania “Dutch” (a corruption of the German word “Deutsche,” which literally means German) were a vibrant immigrant community active in southeastern Pennsylvania in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. By 1790, they made up about forty percent of the population and vied with those of British ancestry as the largest ethnic group. Even in urban areas, such as Lancaster and Philadelphia, the Germans were a sizeable minority.
Within the community itself there was great diversity, although many immigrated from the Palatinate area of southwestern Germany and approximately ninety percent were Protestants, with only ten percent Catholics.
What is remarkable about their legacy is their flamboyant, whimsical, playful, and highly imaginative folk art. They loved to decorate just about every type of household object, from small-scale items like ceramics to large-scale pieces like furniture, with instantly recognizable images. These artists are the most renowned among folk art collectors for their illuminated manuscripts, including marriage and birth certificates, family registers—essentially any type of recorded document. These pieces are called Fraktur.
The Compositions:
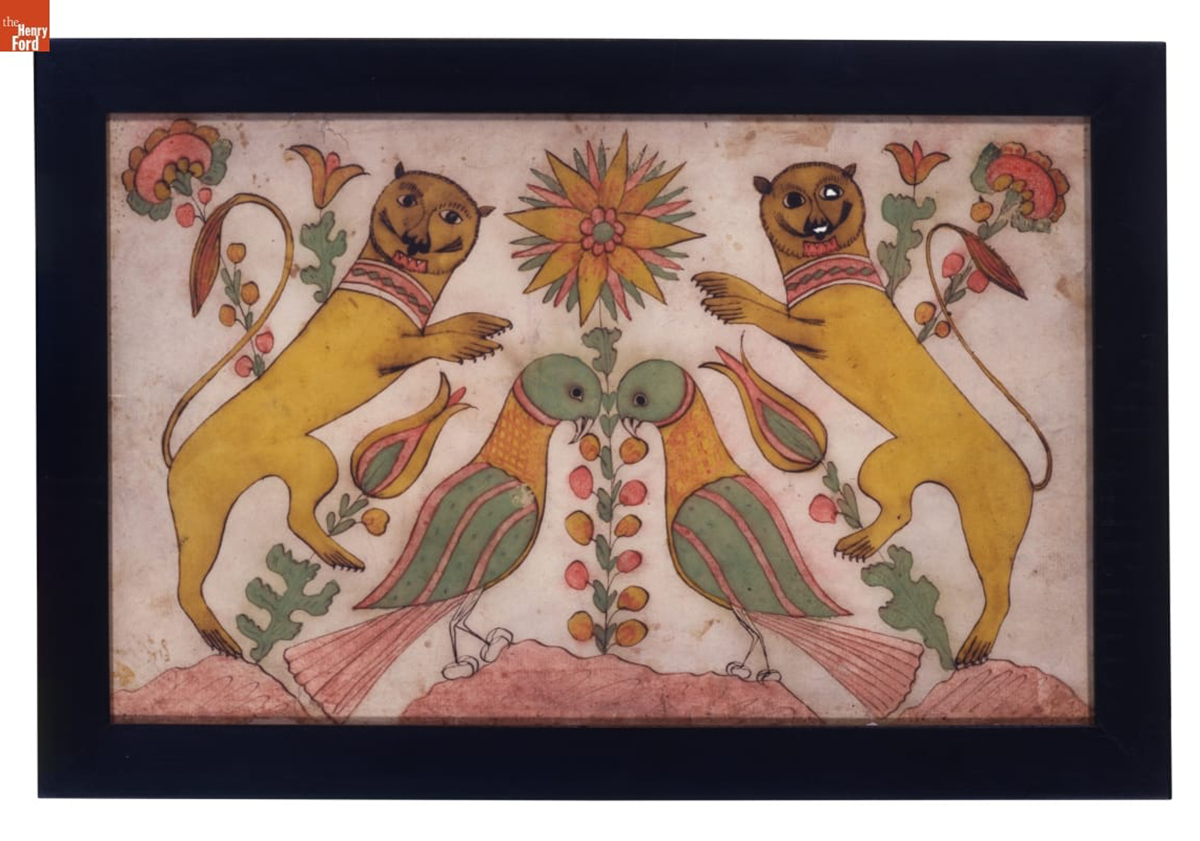

Confronted Lions and Birds, 1800-1820, made by Daniel Otto (active c. 1792-1822) Haines Township, Centre County, Pennsylvania, pen and ink and watercolor on woven paper, 00.3.3038 / THF119526
This Fraktur by Daniel Otto features a stylized central flower where everything on either side balances completely. This symmetry is the hallmark of folk art in general, and Pennsylvania German art in particular. Also note the whimsy or playfulness in the lions—they hardly look ferocious. This is yet another characteristic of Pennsylvania German art.
Decorative Motifs:

A New Year's Wish for Jacob Grimm and Family, circa 1775, made by Daniel Schumacher (active 1728–1787), worked in Berks, Lehigh, and Northampton Counties, 82.114.5 / THF305642
Notice that this piece, essentially an 18th-century New Year’s card, is symmetrically arranged around the text in the center. The highlight is the angel at the top. What is remarkable are the floral elements on either side. Tulips and stylized flowers are iconic design elements that appear in virtually every piece of Pennsylvania German art.
Another good example is this ceramic storage jar:
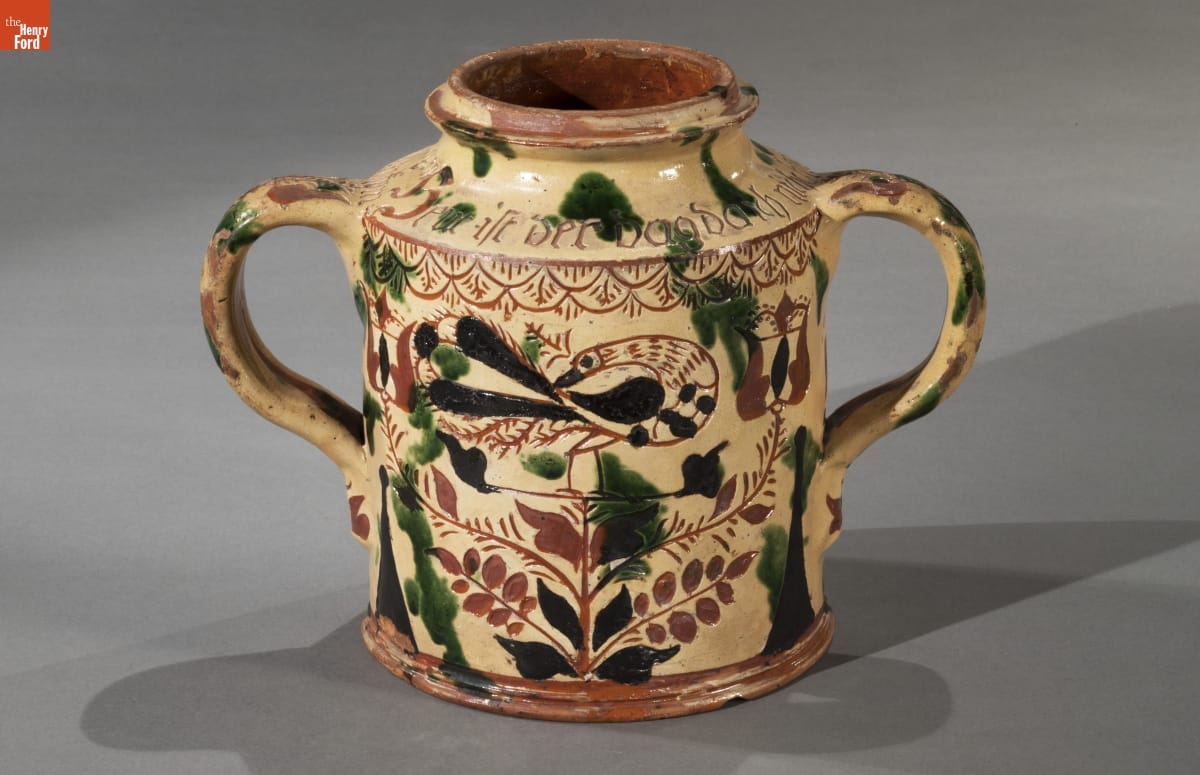

Storage jar, made between 1785-1796, made by George Hubener (1757-1828) Limerick Township, Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, 59.134.1 / THF177128
At the center of this jar, we find another peacock—which are in fact the 'confronted birds' in the second image above. Here, peacocks stand on the branches of a tree or bush. Notice that on either side, the floral branches terminate in tulip blossoms. Like peacocks or other stylized birds, the tulip is a motif frequently seen in Pennsylvania German folk art.
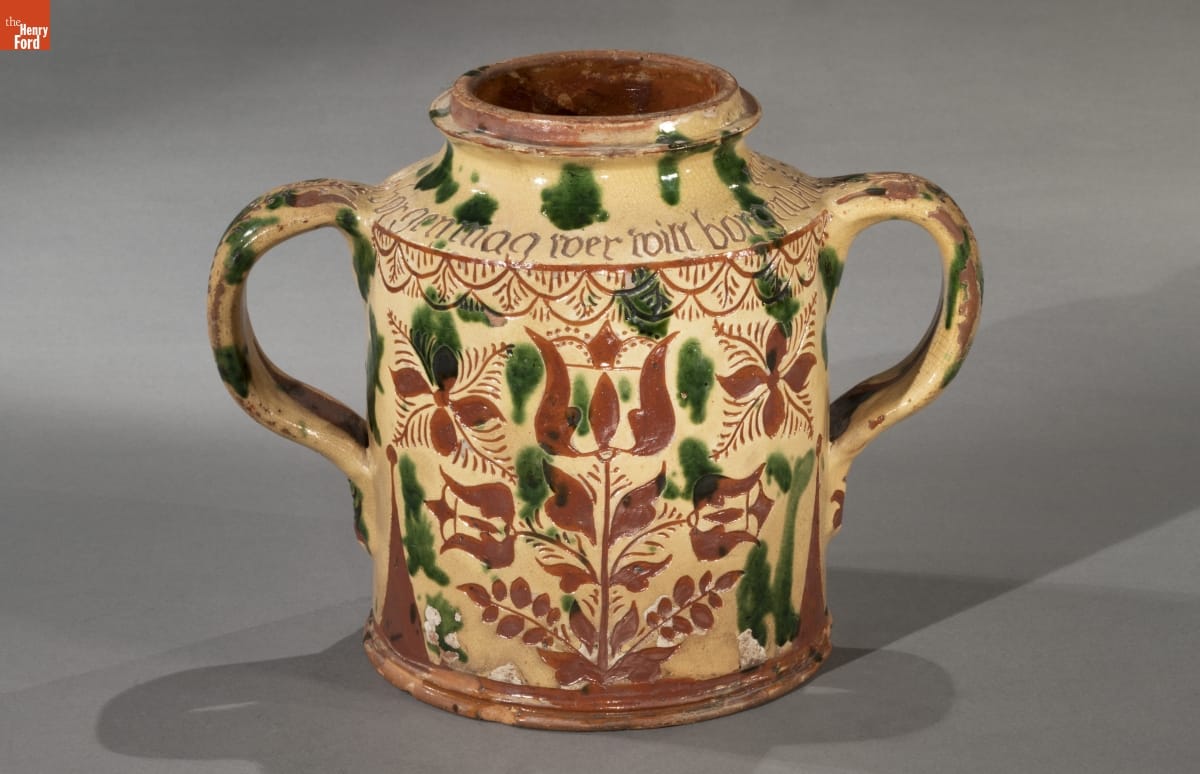

Reverse side of Storage jar, made between 1785-1796, made by George Hubener (1757-1828), Limerick Township, Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, 59.134.1 / THF177132
When we look at the reverse side of the jar, we see a variation of the image on the front. Of course, everything is arranged symmetrically, but instead of a bird at the center, we find a tulip blossom in its place. The space where the tulips were on the front side is now filled with abstracted floral elements.
The same use of symmetry is visible in this image of confronting peacocks:
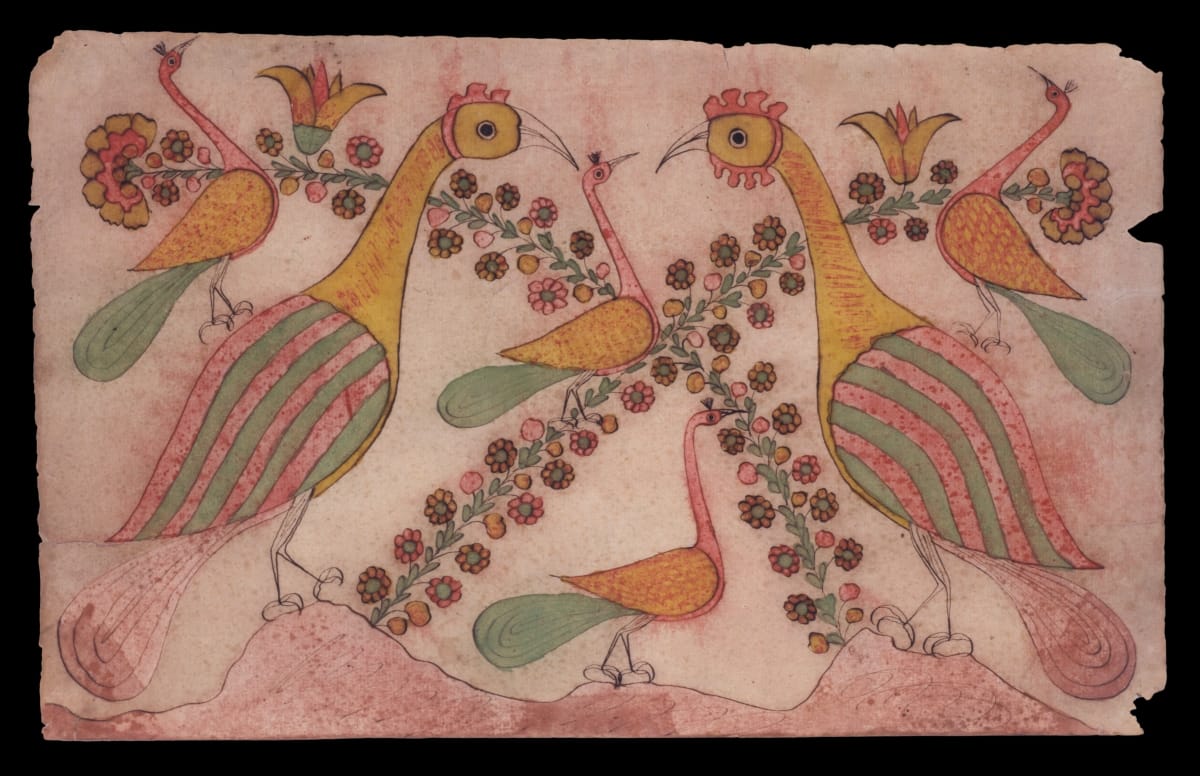

Confronted Peacocks, 1800-1820, made by Daniel Otto (active c. 1792-1822), Haines Township, Centre County, Pennsylvania, pen and ink and watercolor on wove paper, 29.2085.1 / THF119532
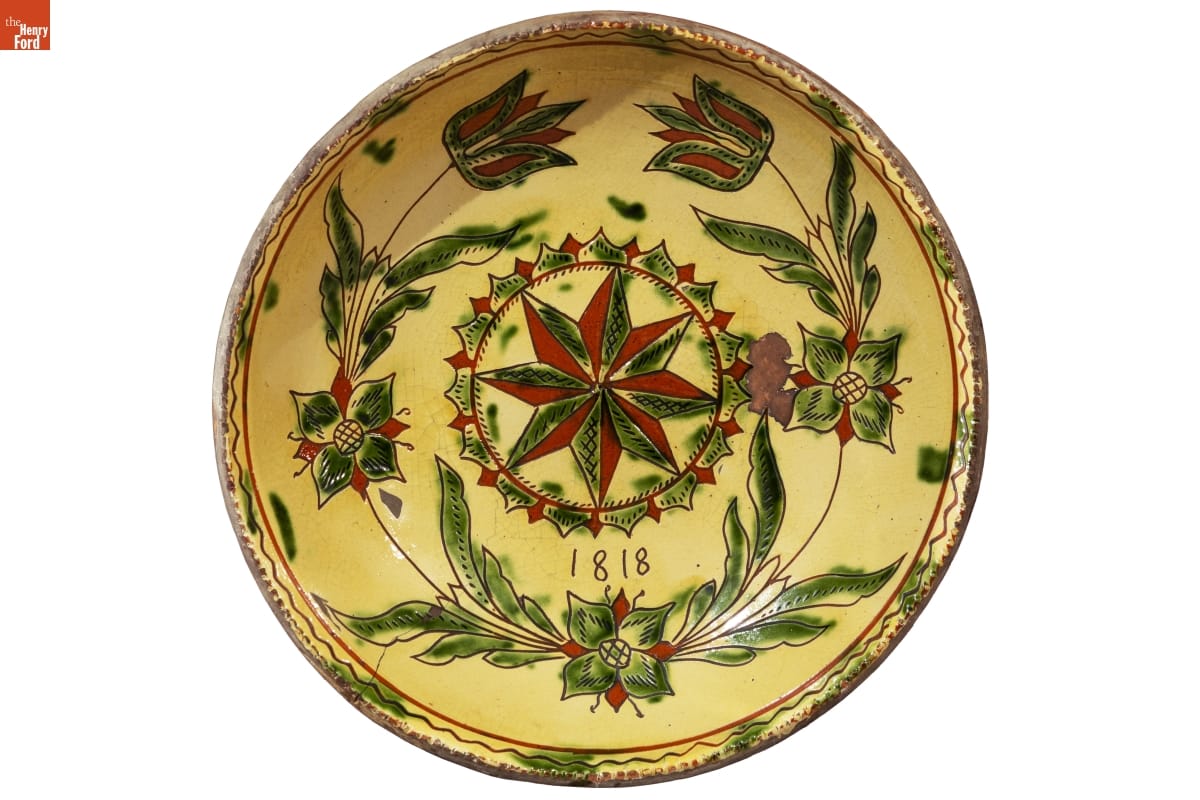

Plate, dated 1818, made by Andrew Headman, (active about 1756-1830), Rockhill Township, Bucks County, Pennsylvania, 56.54.1 / THF191114
This large plate, used primarily for decoration, is once again highly ornate, with a stylized star at the center. This is surrounded by a circle of triangles in red and green, which in turn is circled by a symmetrical row of ubiquitous tulips.
Furniture:

German American Wardrobe 1790-1800 59.80.1 / THF118499
Like all the examples we’ve seen, this wardrobe is decorated with flowers—some naturalistic, some stylized. It also uses reds against greens, like the plate above. Although called a wardrobe, or Schrank in German, it likely was used in a public room, like a parlor or dining room, where it was meant to impress guests. Of all the examples of Pennsylvania German folk art in the Museum’s collection, this is by far the largest and most impressive.
The Spreading Influence:
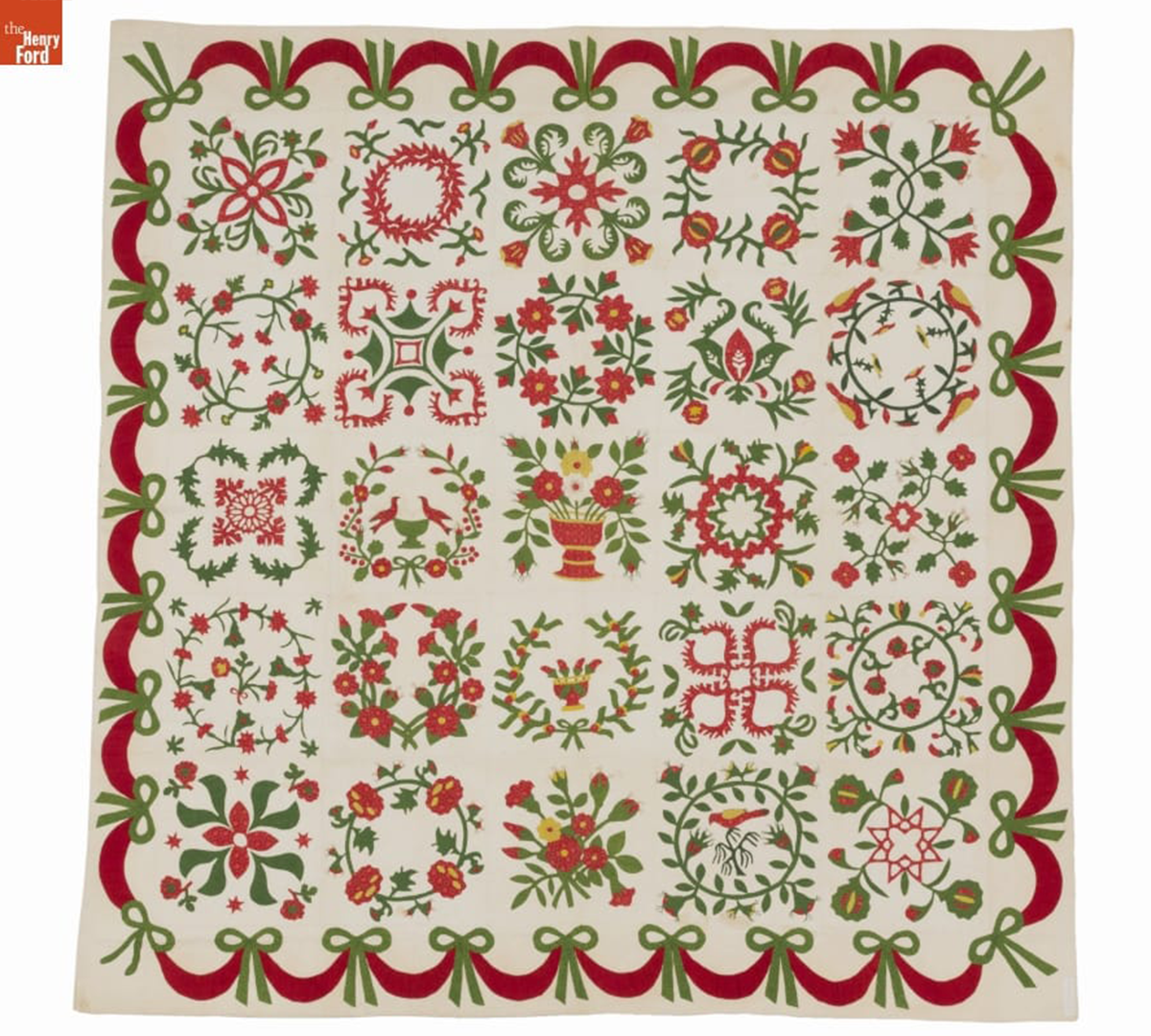

Album Quilt, probably made in southeastern Pennsylvania (perhaps in Chester County), circa 1850. One corner of this quilt carries an applied fabric strip with the inked inscription "Anne D. Morrison." 2016.22.1 / THF166494
By the middle of the 19th-century, the design vocabulary of the Pennsylvania Germans spread well beyond their community, encompassing the entire region. For example, we know that this “Album” quilt that utilizes the Pennsylvania German aesthetic was used by Anne Dawson Morrison (1798-1866), a prosperous Philadelphia Quaker.
These objects are just a small sampling of the large folk art collection of The Henry Ford. To see more, please go to https://www.thehenryford.org/collections-and-research/digital-collections/.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford. Many thanks to Rachel Yerke-Osgood, Associate Curator at The Henry Ford, for editorial preparation assistance with this post.
Tiffany Glass in American Culture
Louis Comfort Tiffany (1848-1933) transformed the glass world with his patented Favrile process, which created a shimmering, iridescent effect, in the 1890s. More than a century later, Tiffany remains a household name, conjuring images of iridescent stained-glass windows and lighting. How has Tiffany stood the test of time?

Daffodil table lamp, designed by Clara Driscoll for Tiffany Studios, 1903-1920. / THF167923
Tiffany worked with the leader of the Art Nouveau movement in Paris and became internationally renowned in the 1890s. Competing European glassmakers took inspiration from Tiffany, and rivals in the American market worked to develop wares that were almost indistinguishable from his — all helping to establish Tiffany as the look in art glass. Tiffany famously applied Art Nouveau aesthetics to lighting, creating what would become the iconic “Tiffany lamp.”
American tastes changed after World War I as people began searching for something modern and different in their décor. A new geometric style called Art Deco emerged, but Tiffany products remained rooted in the now-passé Art Nouveau. Sales plummeted in the 1920s, and the Great Depression finally shuttered Tiffany Studios. One scholar noted that Tiffany lamps, vases and decorative objects became fodder for tag and rummage sales. Nevertheless, influences of Tiffany’s aesthetic lingered throughout the 1930s and 1940s.

This 1930s White Castle sign shows Tiffany’s lingering influence. / Detail, THF101929
In the 1950s, museums began reevaluating Tiffany’s contributions to American culture. In 1955, the Morse Gallery of Art in Winter Park, Florida, organized "Works of Art by Louis Comfort Tiffany," the first solo exhibition of Tiffany since his death. Others, including Henry Ford Museum, began collecting Tiffany objects as early as 1954. By 1959, the prestigious Museum of Modern Art in New York included Tiffany glass in its modern design gallery and produced a groundbreaking exhibit, "Art Nouveau: Art and Design at the Turn of the Century." This reappraisal led to the beginning of new scholarship on Tiffany and a broader market for art glass among collectors from the 1960s onward.
The revival of interest in Tiffany's work — and in Art Nouveau in general — came into vogue through the counterculture of the 1960s. Just as before, a younger generation sought out new directions in material culture. In this, they referenced just about anything that rebelled against the prevailing minimalism of mid-century modernism. The highly decorative and organic qualities of Tiffany glass appealed to them.

The sense of nostalgia evoked by hippie culture appeared early on in mainstream material culture through old-fashioned ice cream parlors like Eurich's in Dearborn, Michigan, seen here circa 1962. Note the Tiffany-style lighting above the counter. / THF147849
By the early 1970s, Tiffany was more than a name — it was a style. Tiffany lamps reached the height of their popularity. And with the United States Bicentennial in 1976, Americans became even more enamored with the nostalgia of the American past. This led many companies to embrace an old-fashioned look that often included Tiffany-style lighting — the sort that filled early Wendy’s fast food restaurants, for example.

In the 1970s, Tiffany became fully diffused in American mainstream culture, as evidenced by Hallmark’s Tiffany Classics series of holiday ornaments. / THF177479
This nostalgia continued throughout the early 1980s but began to wane over the course of the decade. Yet even as the Tiffany style faded from fashion, it remained a cultural icon.
Charles Sable is curator of decorative arts at The Henry Ford. This post was adapted for the blog by Saige Jedele, associate curator.
Pyrex, Corning Ware and Corelle: Enduring Kitchen Icons from Corning
Three brands developed by Corning Glass Works during the 20th century — Pyrex, Corning Ware and Corelle — became household names that revolutionized American kitchens and endured decades of changing consumer tastes and expectations.

Corning Glass Works found both industrial and household applications for Pyrex. The company produced Pyrex insulators and laboratory glassware alongside its increasingly popular ovenware in the 1930s. Pyrex Perfect Antenna Insulator, 1930-1939. / THF174626
In 1908, scientists at Corning developed glass that could withstand extreme temperatures. It was initially used for industrial products like railroad lanterns and battery jars. Hoping to broaden the market, Corning spent years testing possible household applications. Encouraged partly by the success of one notable experiment — when Bessie Littleton, whose husband was a Corning researcher, used a modified glass battery jar to bake a cake — Corning introduced Pyrex, a line of temperature-resistant glass cookware. The launch of Pyrex in 1915 inaugurated a new Corning division dedicated to consumer products.

This early advertisement for Pyrex ovenware touts its many advantages. National Geographic, 1916. / THF709296
Pyrex bakeware entered the market at an advantageous time. In the early 20th century, the principles of scientific management — used in industrial settings to improve efficiency — found their way into the kitchen. Transparent Pyrex ovenware fit the bill — it performed well, was easy to clean and could go from oven to table. The Pyrex line was expensive at first — marketed initially to women of means interested in up-to-date products.

Pyrex Flameware Percolator, 1939-1951. / THF191912
Pyrex’s excellent performance in baking was unquestionable. Yet, to become a greater contender in the cookware industry, Pyrex would need to be usable for top-of-stove cooking on an open flame. The introduction of Pyrex Flameware in 1936 added this feature, increasing the product’s appeal. Too, changes in manufacturing helped make Pyrex more affordable by the 1930s.
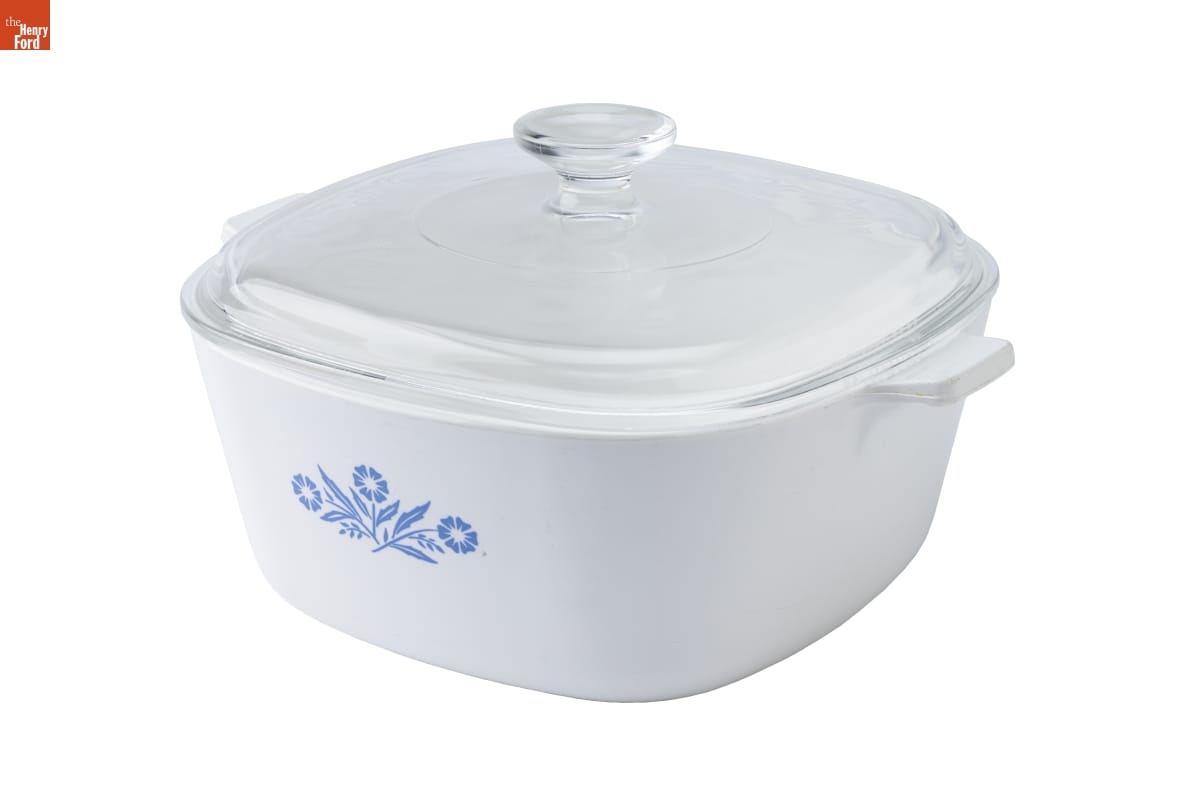

Corning Ware Casserole Dish, 1960-1961. / THF192899
Next up? The accidental discovery of a new material — glass-ceramic — by a Corning research chemist in 1952. The gleaming white opaque material could withstand extreme cold and heat and didn’t break when dropped. First used in nose cones for radar-guided missiles, this new material found its way into the kitchen in 1958 as Corning Ware — a line of innovative, shatterproof cookware that could go right from the freezer to the oven or range and then to the table as a serving dish.

Corning advertisement, 1968. / THF710401
Versatile, durable, attractive and affordable, Pyrex and Corning Ware became staples in American kitchens.
Color and More

Pyrex Primary Colors Mixing Bowl Set, 1949-1957 and three Pyrex Primary Colors Refrigerator Dishes with Lids, 1947-1960. / THF167736, THF176489, THF176490 and THF176488
By the late 1940s, Corning sought to appeal to evolving post-World War II tastes with a focus on the center of the American home — the kitchen. Continuing the trend toward enlivening kitchens with new products in vibrant choices, Corning transformed Pyrex from colorless to colorful with the “Primary Colors” line, introduced in 1947. Customers could mix and match sets of cookware that were practical and functional but also stylish.

Cornflower Pattern Percolator, Teapot and Platter 1960-1961. / THF370218, THF370237, THF191905
Corning applied a similar styling approach to its revolutionary Corning Ware line. The popular Cornflower Blue pattern, introduced in 1958, became synonymous with Corning’s brand identity. It appeared on all sorts of products — most famously on casseroles but also on percolators, teapots and platters. Consumers could buy pieces as needed and eventually collect a color-coordinated set of cooking and serving ware. Later patterns reflected new trends and helped broaden the market for Corning Ware.

This Corning Ware brochure shows patterns available in 1987 — Shadow Iris, Pastel Bouquet, Spice O’ Life and the iconic Cornflower Emblem — as well as the now-classic French White line of casseroles. / THF709300
Revolutionizing the Dinner Table

Corelle Livingware cups and saucers in Butterfly Gold, 1971. / THF195008, THF195009, THF195011
Unlike Pyrex and Corning Ware — products made of new materials created without a singular purpose in mind — Corning deliberately pursued another kitchen innovation in the 1960s. The company thoroughly researched consumer preferences in dinnerware and then set to work on improving it. A breakthrough came in 1965 when a Corning scientist developed a laminating technique that produced very thin, yet very strong glass. Corning introduced Corelle Livingware, dinnerware made from this light and durable layered glass, in 1970.

Corelle Livingware dinnerware set in Spring Blossom Green, 1971. / THF195020
Corelle was a radical departure from the past, where expensive dinner sets consisted of many pieces, including luncheon plates and soup and salad bowls. By contrast, the first Corelle Livingware service consisted of a set of four large plates, four medium bowls, and four cups and saucers, retailing for the attractive price of $19.95. In addition, Corning provided a two-year guarantee to replace any piece that broke.
Corning’s savvy marketers compared Corelle to fine china. Product packaging with the slogan “looks, feels, and rings like china” depicted a mother “pinging” a Corelle plate. The company also offered consumers a selection of fashionable patterns. Pieces from the debut collection featured Butterfly Gold, Spring Blossom Green, Old Towne Blue and Snowflake Blue designs around the rim. Corning’s greens and golds were variations of the Harvest Gold and Avocado Green color schemes iconic of the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Corelle was incredibly successful and changed middle-class American dining habits — it was chic yet durable and inexpensive enough for casual use. Corelle frequently sold out and was back-ordered throughout the 1970s. Corning continually added new “lifestyle” patterns and discontinued old ones to keep up with the latest decorative trends.
Still the Standard

Corning Pyrex FreshLock Plus food storage set with Microban antimicrobial product protection, 2022. / THF195359
Corning continually updated its Pyrex, Corning Ware and Corelle lines with new products that retained the qualities that had made them household names. The company sold its housewares division in 1998, but all three brands remained staples of American kitchens. In the 21st century, updated variations and marketing approaches appealed to changing tastes and lifestyle trends. Sets of Pyrex dishes designed for cold storage, portability and easy reheating featured locking plastic lids with odor-preventing technology. Marketers imagined new uses for classic Corning Ware, even designating some iconic French White casseroles as official companion pieces for the cult favorite Instant Pot brand of multicookers. (The company that manufactured Corning housewares merged with Instant Brands in 2019.) Continually updated Corelle patterns appealed to contemporary tastes.
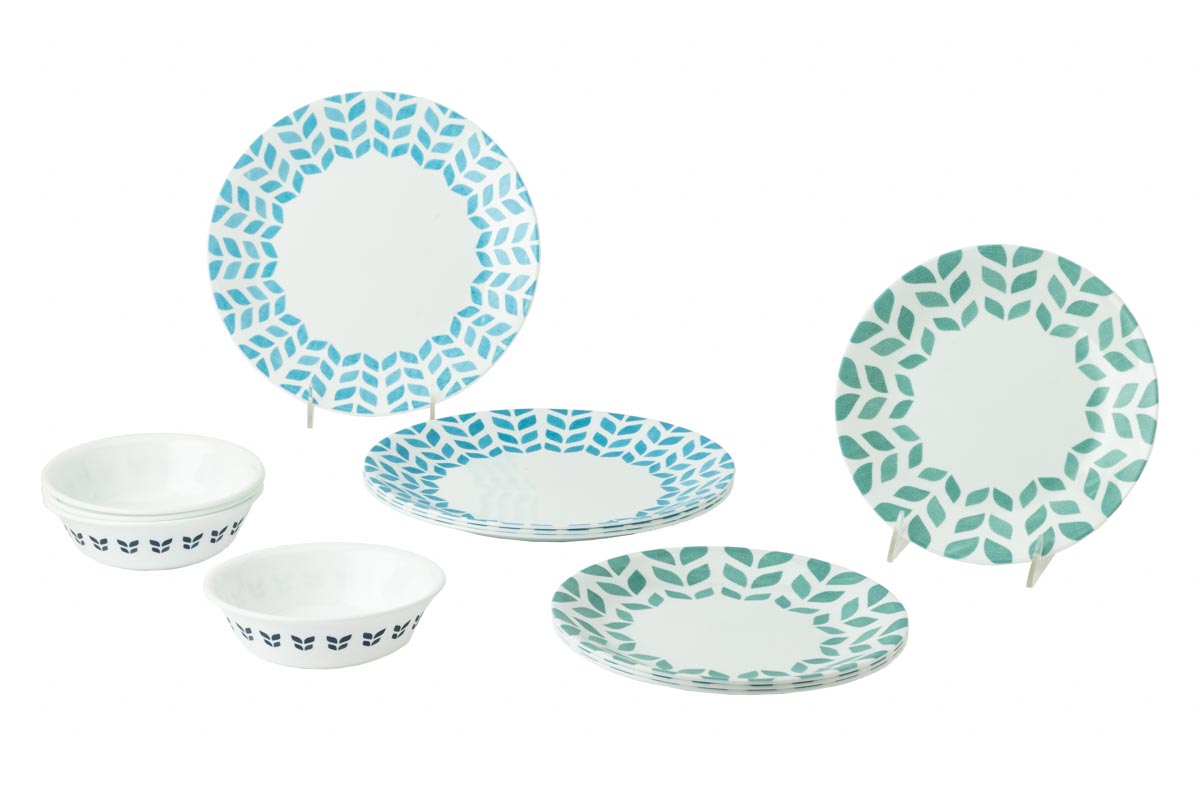

Corelle Livingware dinnerware set in Northern Pines, 2022. / THF195362
Durable, convenient and stylish, the iconic brands developed by Corning in the 20th century continue to have relevance in today’s kitchens.
Charles Sable is curator of decorative arts, Jeanine Head Miller is curator of domestic life and Saige Jedele is associate curator at The Henry Ford.
glass, by Jeanine Head Miller, by Charles Sable, 20th century
Western Interactions with East Asia in the Decorative Arts: The 19th Century
Western Europe and its former colonies in the Americas were long fascinated with the Eastern cultures Europeans depicted as “mysterious”—specifically their exotic and luxurious trade goods. This is the second of two blog posts that examine this European and American fascination with Asia and the way that was expressed in the decorative arts. In the first post, I discussed the China trade in the 17th and 18th centuries, specifically Chinese export porcelain and the related tea trade. This post focuses on the 19th century, with the decline of the China trade, the opening of Japan to the West, Western eclecticism in the decorative arts, and the beginning of Western understanding of Asian design.
The China Trade in the First Half of the 19th Century
By the early 19th century, Europe and America had learned the secret of “hard paste” or true porcelain, so Westerners could produce their own high-quality wares. In the early American republic, porcelain factories popped up as early as the 1820s. This is not to suggest that that trade in Chinese porcelains declined; rather, it entered a new phase.
Canton Ware Serving Bowl, 1800–1850 / THF160724
The serving bowl above would have been a prized possession of an American family in the first half of the 19th century. Part of a dinnerware set, this Canton ware, or “Blue Willow,” pattern appealed to middle-class Americans as an example of the exoticism of a faraway place, and implied the owners’ good taste and sophistication. Compared with the expensive and highly prized 18th-century wares, Canton china was inexpensive. This porcelain was shipped from Guangzhou, then called the Port of Canton by the English, to serve as a ship’s ballast under the more valuable tea chests.
Canton Ware Serving Bowl, 1800–1850 / THF160723
These wares usually depict a landscape with Chinese buildings and a bridge in the center and have a decorated rim. This pattern was widely copied by English makers in the late 19th and 20th centuries and became so inexpensive that it was sold at five-and-ten cent stores in the 20th century. This example is interesting as it broke at some point during its working life and was mended with visible staples, indicating that it was indeed a valued possession.
Watercolor Painting, Two Rooms of a Chinese Painter's Studio, circa 1865 / THF119916
The remarkable image above shows the interior of a Chinese porcelain studio, with craftspeople decorating ceramics for the Western market. Visible on the wall on the left are prints or drawings supplied by Western agents, which were then copied by the artists in the foreground. The table on the right is filled with finished pieces of decorated ceramics. This piece itself was a souvenir intended for the Western market.
While the China trade continued throughout the 19th century, imports to America declined with the Civil War in the 1860s and never rebounded. After the Civil War, the United States and Europe became fascinated with another Asian nation, Japan.
Japan and the West
Japan, like China, traded with the Spanish, Portuguese, and Dutch beginning in the 15th century. However, by the middle of the 17th century, Japanese authorities closed their doors to Europeans, primarily due to the undue influence of Catholic and Protestant missionaries. In 1853, the American Commodore Matthew Perry, under the direction of President Millard Fillmore, arrived in Yokohama harbor with a fleet of steam ships, which impressed the Japanese with their high degree of technology. The Japanese grudgingly agreed to open their markets to the Americans and the West. During the next few decades, traditional Japanese arts flowed to the West, where they profoundly influenced European and American fine and decorative arts.
Japanese River Scene Wood Block Print, 1900–1929 / THF292625
Japanese Travelers in a Snow Storm, Wood Block Print, 1900–1929 / THF292633
The wood block prints above are good examples of Japanese exports that excited Western artists and designers. The compositions were like nothing ever seen in Europe or America. The use of flat, unmodulated colors laid down next to each other, combined with diagonals, provided a sense of depth. This influenced the Impressionist and Post-Impressionist artists in France and designers everywhere.
Folding Side Chair, 1880–1885 / THF92166
The influence of images from Japanese prints on Western decorative arts can be seen in the carved cranes on the side chair above, painted in black to imitate ebony, an expensive wood that late Victorians associated with Japan. This is known as Anglo-Japanese style, which began in England in the 1870s and spread to America by the 1880s. Like many of the Asian imports, this Western style had little to do with Japan itself; rather, it suggested the “exoticism” of the Far East.
Pitcher, 1870–1875, Made by Tiffany and Company, New York, New York / THF190746
Like the side chair, Tiffany and Company’s elegant silver pitcher uses stylized images of birds and foliage done in the Anglo-Japanese style.
Floral Wallpaper Sample, 1860–1880 / THF190058
Floral Wallpaper Sample, 1860–1880 / THF190057
Wallpaper Sample, 1880–1890 / THF190054
The highly stylized wallpapers shown above were derived from the floral patterns of Japanese prints. European and American designers called these abstracted patterns “conventionalized” ornament. These wallpapers appealed to those interested in what was called the “aesthetic” taste. This taste tended to be high style, although by the 1880s, middle-class Americans applied elements of it in their interiors. For example, the sample above was found in the middle-class Firestone Farmhouse, now in Greenfield Village. The date of our interpretation is 1885.
Eclectic Design in the Late 19th Century
What we’ve looked at so far has imagery directly linked to either Chinese or Japanese originals, but there is another category of decorative objects that contain more interpretive elements derived from Chinese, Japanese, or other Asian designs. Some of these pieces contain imaginary elements that the designer created out of thin air.
“Crown Milano” Vase, 1888–1893, Made by the Mount Washington Glass Company, New Bedford, Massachusetts / THF163595
“Burmese” Caster, 1885–1895, Made by the Mount Washington Glass Company, New Bedford, Massachusetts / THF167758
The ornate and elegant glass pieces above are clearly influenced by Japanese designs but have been transformed by late-19th-century American glassmakers into something unique. They are highly decorative and distinctly of their time.
Silver Tea Caddy, 1875, Made by the Gorham Manufacturing Company, Providence, Rhode Island / THF190070
Tea and Coffee Service, 1883–1884, Made by Gorham Manufacturing Company, Providence, Rhode Island / THF154882
In the late 19th century, wealthy Americans demanded ornate silver sets, and above are notable examples of just how wild they could get. The tea caddy references Asian design elements—as perceived by Americans, who had little true understanding of Asian cultures. Likewise, the full tea set picks up on the Anglo-Japanese style, but takes it much farther, into something truly Victorian—and, like the glass examples, totally unique.
Attempts at Understanding Asia

Vase, 1896–1908, Made by Hugh Robertson at the Dedham Pottery, Dedham, Massachusetts / THF176707
By the beginning of the 20th century, there were several designers looking for true sources of inspiration in Asian design. One of the most interesting of these was the English-born potter Hugh Robertson (1845–1908). During his time at the Dedham Pottery in Massachusetts, Robertson was obsessed with recreating the well-known Chinese oxblood glaze, seen on the vase above. He spent decades experimenting and perfecting the glaze, first at his family's Chelsea Keramic Art Works and later at Dedham. He was also interested in recreating the forms of Chinese porcelain made for domestic production rather than for export.
I hope you have enjoyed this quick journey through The Henry Ford's collection of Asian-influenced decorative arts. All of these artifacts, as well as many more, are available for browsing online in our Digital Collections.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford.
Additional Readings:
- Davidson-Gerson Modern Glass Gallery
- Digitizing Our Newest Exhibit
- Photographing Glass
- Artist in Residence: Shelley Muzylowski Allen
Europe, 19th century, Asia, paintings, glass, furnishings, design, decorative arts, ceramics, by Charles Sable, art
The Scottie Dog: Icon of an Age
During the 1930s and 1940s, Scottish Terriers, or “Scotties,” popped up all over popular culture, from jewelry to ceramics to greeting cards. I've found various types of Scottie memorabilia in The Henry Ford's collections of this period. The question is, why were Scotties so popular?
According to the American Kennel Club, Scottish Terriers first became popular in America in the early 20th century, with the “Golden Age” arriving in the 1930s. This may be due to the personality of Scotties. The American Kennel Club references this description of the Scottish Terrier’s temperament: “Contented in his ways, conscious of the affection he bears to master or mistress, he regards life philosophically, takes the best when he can get it, makes the best when he cannot.”
Of course, the 1930s represents one of the most desperate economic periods in American history: the Great Depression. It makes perfect sense that Americans loved the spirited Scottie during this dark time.
Also, celebrities as diverse as Bette Davis, Dorothy Parker, Charles Lindbergh and Anne Morrow Lindbergh, and Humphrey Bogart adopted Scotties and helped make them popular—both as pets and on memorabilia.
Some of the most common places that they appear are in Christmas cards.
Christmas Card, "A Merry Christmas," 1933 / THF36815
This card shows a pair of mischievous Scotties, one of whom shows us a Christmas stocking with a puppet tumbling out of it.
"Scottie" (Scottish Terrier) Napkin Rings, 1930-1950 / THF189764
Plastics were used for inexpensive items such as these adorable napkin rings, likely purchased at a five-and-ten-cent store. They would have brightened up a Depression-era dining room table.
"Scottie Dog" Cigarette Holder and Ash Trays, 1935-1940 / THF169674
This inexpensive, yet fashionable, ceramic cigarette set, like the napkin rings, was likely retailed at a five-and-ten-cent store. It would have been a novelty or conversation piece in a middle-class living room.
Fala: The Most Famous Presidential Pet

President Franklin Delano Roosevelt with Fala, 1940 / Photo from the Franklin D. Roosevelt Presidential Library & Museum
The photograph above shows President Franklin Delano Roosevelt with his new Scottish Terrier, Fala, a gift from Roosevelt’s cousin, Margaret “Daisy” Suckley. Was Roosevelt aware of the popularity of Scotties, or was it just serendipity? Probably a little of both. Fala was named by Roosevelt after a Scottish ancestor, the “outlaw” John Murray of Falahill. “Murray the Outlaw of Falahill” was soon shortened to “Fala,” and like his namesake, the Scottie's legend grew. Fala’s adorable antics soon made him popular, and perhaps beloved, by the White House press corps.
Fala “Photographing” White House Photographers, 1942 / Photo from the Franklin D. Roosevelt Presidential Library & Museum
Fala and the Barkers for Britain Campaign
As you can see, Fala’s instant fame, plus national interest in Scottish Terriers, created a public relations bonanza. During 1941, as World War II raged in Europe, the Roosevelt administration sought to help Great Britain, the lone country in Western Europe left standing against the forces of Nazi Germany. Although the United States was officially neutral, many Americans sympathized with and sought to aid the British. They were led by the British War Relief Society, an umbrella organization based in New York City. A constituent group called “Bundles for Britain” collected clothing and money for humanitarian aid. “Barkers for Britain” was created for dog lovers, with paid memberships benefiting the Bundles group. For a fee of 50 cents, dog owners could get a tag with their dog’s name inscribed with a Barkers for Britain label. President Roosevelt volunteered Fala as president of the group, and Fala got membership tag number one.
Christmas Card, "Cheerio," 1941 / THF702390
Interior of Christmas Card, “Cheerio,” 1941 / THF702391
Dating to 1941, this Christmas card references Scottish Terriers and Britain, with “Cheerio” on the outside and “The Englands” on the inside.
Fala’s Moment of Fame in 1944
As a favorite companion, Fala was constantly by Roosevelt’s side. He traveled everywhere with the president. In the late summer of 1944, with the United States now fully engaged in World War II, Fala accompanied Roosevelt on the USS Baltimore to Hawaii, where Roosevelt met with General Douglas MacArthur and Admiral Chester Nimitz on plans to retake the Philippines and attack the Japanese mainland. The Baltimore then traveled to the Aleutian Islands off the coast of Alaska, where Roosevelt met with local leaders on asserting American control over islands that had been taken by the Japanese early in the war. The ship returned to the American mainland via Seattle, where Roosevelt and Fala took a train back to Washington, D.C.
In 1944, a presidential election year, Roosevelt was seeking an unprecedented fourth term. Republicans sought any “dirt” they could find on Roosevelt, an extremely popular Democrat and president since 1933. It is unclear how the rumor got started, but Republicans began circulating a story that Fala had been left behind in the Aleutian Islands and a destroyer had been sent from Seattle, at taxpayers’ expense, to retrieve him. Roosevelt was accused of wasting some 20 million dollars in this effort. Ever the canny politician, the president used this to his advantage. Speaking to the Teamsters Union while kicking off his reelection campaign, Roosevelt gave a speech that many say ensured his reelection. Here is an excerpt:
"These Republican leaders have not been content to make personal attacks upon me—or my wife or my sons—they now include my little dog, Fala. Unlike the members of my family, Fala resents this. When he learned that the Republican fiction writers had concocted a story that I had left him behind on an Aleutian Island and had sent a destroyer back to find him—at a cost to the taxpayer of two or three or twenty million dollars—his Scottish soul was furious! He has not been the same dog since."
Not only did Roosevelt get a positive reaction from his Teamster audience, but he was also heard on radio from coast to coast. The voting public realized that the president still had fight in him and that his feisty little dog was a great asset. As part of the Roosevelt campaign, young girls began sporting Scottie dog pins, like this one.
"Scottie" (Scottish Terrier) Pin, circa 1940 / THF30462
In a broader context, Fala started the tradition of presidential pets serving as surrogates in the political arena. Some notable examples include Richard Nixon’s famous “Checkers” speech in 1952 and Socks the cat, the pet of Chelsea Clinton, daughter of Bill Clinton, in the 1990s. Nearly every president since 1944 has attempted to promote his pets, but none have done so as deftly as Roosevelt.
Eleanor Roosevelt with Fala, 1951 / Photo from the Franklin D. Roosevelt Presidential Library & Museum
After Roosevelt’s sudden death in April of 1945, Fala lived with Eleanor Roosevelt at the family’s Hyde Park, New York, home until the dog’s own death in 1952. At Roosevelt’s memorial in Washington, D.C., the president is depicted with Fala at his side.
Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial, Washington, D.C., 2016 / Photograph by Ellice Engdahl
The Scottie dog is truly a reflection of American life at a difficult period, when tenacity, good spirits, and a can-do mentality helped the nation survive and ultimately prosper.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford.
Washington DC, 1940s, 1930s, 20th century, World War II, presidents, popular culture, home life, decorative arts, by Charles Sable
The earliest form of decorative arts that fascinated Europeans was porcelain. Around the 7th or 8th century C.E., the Chinese first produced what Westerners call “hard paste” porcelain—clay that consists of a compound containing the mineral kaolin and is fired at an extremely high temperature, usually around 1400 degrees Celsius. The kaolin in the clay fused the body with the glaze on top during the firing process. The resulting vessel proved to be extremely durable, almost glass-like, and resisted chips and cracking. Should the piece break, it would be a clean break.
Western ceramics were mostly made from earthenware, usually fired at a relatively low temperature with a slip (watered-down clay) glaze or a true glaze. Both processes cover the vessel with fine particles which fuse into a glasslike layer, sealing the pores of the clay body. There are two main types of glazed earthenware. The first is covered with a transparent lead glaze, where the earthenware body to which this glaze is applied has a creamy color, known as creamware. The second type, covered with an opaque white glaze, is called tin-glazed earthenware, popularly known as majolica, faience, or delft. Both types of earthenware chipped and broke easily.
When Europeans were first exposed to Chinese porcelain in the 14th and 15th centuries, it was seen as wondrous and innovative. In addition to its glasslike qualities, the pure white color of the porcelain amazed Europeans. In the 16th and 17th centuries, Spanish, Portuguese, and Dutch traders competed to secure Chinese porcelains for the European markets. The teacup shown below is a good example of what the Europeans craved.

Teacup from Vung Tau Shipwreck, Late 17th Century / THF188797

Teacup from Vung Tau Shipwreck, Late 17th Century / THF188796
This teacup was salvaged from a shipwreck dating around 1690 in the South China Sea, about 100 miles from Vung Tau, Vietnam. During the early 1990s, thousands of porcelain items destined for the Dutch market were brought up from the wreck and sold at auction. The Henry Ford acquired this item from one of the auctions. This small cup would have been prized in the household of a wealthy European. It might even have found its way to the American colonies as a luxury item during the late 17th or early 18th centuries.
Items like this teacup provided a design source for European ceramic makers beginning in the late 17th century. Basically, they attempted to appropriate the Chinese designs in earthenware, as in the storage jar shown below.

Storage Jar, 1710-1750, Made in the Netherlands / THF190255

Storage Jar, 1710-1750, Made in the Netherlands / THF190254
What is so interesting about this piece is that the Dutch decorator is drawing Chinese figures in a Chinese inspired landscape for a European audience. Even the form, known as a ginger jar shape, is based on Chinese precedent. The only missing element here is the circular lid. This is helpful for us because the top rim, where the lid should be, shows us the chips in the glaze that occurred though use. We can see that this is not Chinese porcelain, as the dark-colored earthenware body shows through. Chips are also visible along the base. Clearly this jar was not only a prized object but was used.

Punch Bowl, 1700-1730, Made in England / THF188783

Plate, 1690-1710, Made in England / THF188779
The punch bowl and plate shown above, both made in England, attempt to copy the look of Chinese porcelains—but, like the storage jar, are made of earthenware. We could really call these the first "knock-offs" in history. They represent the beginnings of what collectors and scholars call “Chinoiserie”—the appropriation and interpretation of Chinese and East Asian design motifs by Europeans. The idea was to create the spirit of a faraway place and give the owner the cachet of owning a luxurious and expensive object. The underlying idea was to project a sense of worldliness and sophistication.

Tea Box and Cannisters, 1800-1840, Made in China for the Western Market / THF190059

Tea Caddy, 1740-1770, Made in England / THF189630
During the 17th and 18th centuries, tea from China became an important trade good, especially in England and America. Elegant Chinese lacquer boxes, complete with Chinoiserie scenes, became the rage, as did tea caddies, a necessary part of a tea set designed to safely store and dispense tea leaves.

Tea Service, 1765–1770, Made by the Worcester Porcelain Company, Shropshire, England / THF154881
In the later 18th century, tea equipment became extremely sophisticated, as the set above shows. This service uses Chinese or Chinoiserie decorative elements and combines them with the popular French Rococo decorative style to a luxurious effect. The English Worcester Porcelain Company tried to imitate Chinese porcelains with their “soft paste” porcelains, which were close approximations of the true “hard paste” Chinese wares. By 1800, the chemistry of Chinese porcelains was known in Europe—first by the Meissen firm in Germany, then later spreading out across the continent.

Western Tea Pots and Slop Bowl in Silver Next to Chinese Versions in Porcelain, Late 18th Century / THF139315
An interesting aspect of the China Trade was the production of Chinese versions of Western forms in porcelain. Western traders or agents, known as “supercargoes,” brought examples of Western wares for copy to Guangzhou (then called the port of Canton by the English). There, they presented them to their Chinese counterparts, who took these items to the porcelain factories located in Jingdezhen, then the porcelain capital of China.

“Hong” Bowl, about 1780, Made in China for the Western Market / THF190085

“Hong” Bowl, about 1780, Showing Trading Offices, Indicated by the Flags of Great Britain, the Hanseatic League (Now Germany), and Sweden / THF190086

“Hong” Bowl, about 1780, Showing the Port of Guangzhou and the Trading Office of Denmark, Indicated by the Flag / THF190088
One of the most interesting aspects of the China Trade was souvenir “Hong” bowls that showed panoramic views of offices, warehouses, and living spaces for foreign merchants in Guangzhou in the late 18th century. These were brought back to the West by supercargoes and used for serving punch at parties. Western merchants were allowed access only to the port area and needed Chinese intermediaries to send their orders to the porcelain factories inland.
In addition to porcelain tea and lacquerware, Westerners sought out luxurious Chinese silks, but relatively little else was imported to the West. One exception is the teapot shown below, made of a Chinese alloy of nickel and copper known as Paktong that resembles silver. In fact, the term “Paktong” is a corruption of the Chinese “bai tong,” meaning “white copper.”

Teapot with Stand, Made for Export, circa 1800 / THF92948
This teapot, made around 1800, was created for sale in the newly independent United States. Following the Revolutionary War, Americans were eager to establish international trade, and the lucrative China Trade was at the top of their list. This teapot would have appealed to Americans as it was executed in the fashionable Federal or Neoclassical style, which emphasized geometric forms, ovals, and cylindrical shapes.
By 1800, the China Trade began to transform. The American market broadened the China Trade, especially as the 19th century progressed and the United States grew. Also, Chinese goods were no longer viewed as unique and luxurious, as they were in the 18th century. This is partly due to the Western discovery of true or “hard paste” porcelain. The Chinese monopoly was gone. Still, Asian goods were depicted as exotic and the romanticized mystery of the Far East continued. In a second installment of this story, we will examine the transformation and role of Japanese influence on the West in the later 19th century.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford.
Additional Readings:
- Build a Model T: Make, Build, Engineer
- The Wool Carding Machine
- Women in Industry and at Home in WWI
- The Hitchcock Chair: An American Innovation
18th century, 17th century, Europe, Asia, manufacturing, making, home life, design, decorative arts, ceramics, by Charles Sable
When thinking about the celebrated figures in decorative arts history, one first thinks of individuals like Thomas Chippendale, Duncan Phyfe, and Gustav Stickley in furniture, Paul Revere and Tiffany and Company in silver, and Josiah Wedgwood in ceramics. All these prominent figures have something in common—they all are men. There are few celebrated female leaders in the decorative arts. This may be due to the scholarly focus on great men, to the detriment of women, until recent years.
Cover of Tried by Fire by Susan Frackelton, 1886. / THF627718
One of the most important and underrecognized women in decorative arts history was Susan Frackelton (1848–1932). She was a founder of the field of women’s china painting in the 1870s and 1880s. She was also a catalyst in transforming that pastime into a profession with the evolution of china painting into art pottery in the 1890s. Unlike her more famous peers, Susan Frackelton earned her living and supported her family on the proceeds of her publishing, teaching, and collaborations with like-minded artists.
Susan Frackelton faced many challenges in her personal and professional life. In many ways, she was a trailblazer for the modern, independent woman. Only in recent years have her contributions been recognized. Like other major figures in the decorative arts, including Thomas Chippendale, she is best remembered for a publication, her 1886 Tried by Fire. In the introduction, she states, “If the rough road that I have traveled to success can be made smoother for those who follow, or may hereafter pass me in the race, my little book will have achieved the end which is desired.”
Why Was China Painting a Means for Women’s Liberation?
Many factors fueled the growth of amateur china painting in late-19th-century America. As America became wealthier after the Civil War, women of the middle and upper middle classes gained more leisure time for personal pursuits. China painting became a socially acceptable pastime for women because it allowed them to create decorative objects for the home. Further, the influence of the English Aesthetic movement and later the Arts and Crafts movement advocated that the creation of art should be reflected in the home. By the 1870s and 1880s, wealthy women were freer to leave the confines of the home through organizations that they set up to create and exhibit their work.
What Is China Painting?

Pitcher, 1890–1910, decorated by an amateur china painter. / THF176880
This pitcher is a good example of the work of an amateur china painter. The artist would take a “blank”—a piece of fired, undecorated, white porcelain, in this case a pitcher made by the English firm Haviland—and paint over the glaze. These blanks could be purchased in multiples at specialty stores. One of the most prominent of these was the Detroit-based L.B. King China Store. It was founded in 1849 and closed during the Great Depression, about 1932. According to a 1913 advertisement, the retailer sold hotel china, fine china dinnerware, cut glass, table glassware, lamps, shades, art pottery, china blanks, and artists materials. Elbert Hubbard, founder and proprietor of the Roycrofters, a reformist community of craft workers and artists that formed part of the Arts and Crafts movement, wrote enthusiastically about the products of the L.B King China Store: “The store is not only a store—it is an exposition, a school if you please, where the finest displays of hand and brain in the way of ceramics are shown.” A woman seeking to learn about china painting could literally walk into the L.B. King Store and walk out with paints, blanks, and a manual like Frackelton’s Tried by Fire and start painting her own china.
The pitcher above is part of a large group of serving pieces in our collection. Also in our collections is a full set of china decorated by a young woman and her friends who learned china painting at what is now Michigan State University. They decorated the dinnerware service in preparation for the young woman’s wedding in 1911. According to family history, the young woman purchased the blanks at the L.B. King Store.
How Did China Painting Evolve in the Late 19th Century?
During the 1870s, Cincinnati was the center of American china painting. The movement was led by two wealthy women, Maria Longworth Nichols (1849–1932), who later founded the Rookwood Pottery, and her rival, Mary Louise McLaughlin (1847–1939). Both studied with European male ceramic artists who had made their way to Cincinnati. Both evolved from amateur status into extraordinary artists, who moved from painting over the glaze to learning how to throw and fire their own vessels, create designs, and formulate glazes for their vessels. This all occurred during the late 1870s, following a display of ceramic art at the Women’s Pavilion of the 1876 Centennial Exhibition in Philadelphia. Both sought to outdo each other in the formulations of glazes. It is generally believed McLaughlin was the first to learn the technique of underglaze decoration, although Nichols later claimed that she was the first to do so. Nichols’ most important achievement was in creating the Rookwood Pottery in Cincinnati in 1880. It was essentially the first commercial art pottery company in America, and it led the way in the development of new techniques that were widely imitated by other firms. Rookwood and its competitors began to hire women to decorate ceramics, opening a new livelihood for women less well off than Nichols and McLaughlin.
Vase, 1902, decorated by Grace Young, Rookwood Pottery Company, Cincinnati, Ohio. / THF176709
Vase, 1917, decorated by Lenore Asbury at the Rookwood Pottery Company in Cincinnati, Ohio. / THF176918
Tile, 1910–1920, made by the Rookwood Pottery Company in Cincinnati, Ohio. / THF176941
Essentially, through the pastime of china painting, a new industry, art pottery, came into being by 1900. Under the influence of popular magazines like the Ladies’ Home Journal and House Beautiful, Americans eagerly acquired art pottery. In fact, tastemakers like the young architect Frank Lloyd Wright filled his houses with art pottery. He considered it very much part of his total aesthetic. Through the first three decades of the 20th century, art pottery was considered a must in any well-furnished American home. It only fell out of fashion in the 1930s, when the Great Depression drastically altered lifestyles.
How Does Susan Frackelton’s Story Fit into All of This?
Susan Stuart Goodrich Frackelton was a contemporary of both Maria Longworth Nichols and Mary Louise McLaughlin, born in 1848 like Maria Longworth Nichols, and just a year older than Mary Louise McLaughlin. Unlike either of these women, she came from a modest background. Her father was a brick maker in Milwaukee, and she was raised in a middle-class environment. Susan began her artistic career studying painting with the pioneer Wisconsin artist Henry Vianden. In 1869, she married Richard Frackelton and eventually raised three sons and a daughter.
Richard’s business was importing English ceramics and glass and was relatively successful. Within a few years, however, the business began a sharp decline and Susan stepped in to help. She later said that she learned about American taste in ceramics and business while working with her husband. Concurrently, she began to experiment with china painting, applying her experience in painting with Henry Vianden. She was essentially self-taught, unlike her contemporaries in Cincinnati. Through publications, she was aware of what was going on in the field. She was also aware of the innovations of Mary Louise McLaughlin in glazes, and by the late 1870s was experimenting in underglaze painting herself.
Frackelton’s contributions to china painting began in 1877, when she opened Frackelton’s Decorating Works in Milwaukee. She trained young women in the art of china painting. By 1882 she opened a related business called Mrs. Frackelton’s Keramic Studio for Under and Overglaze, where she sold her own work, wares made by her students, commercial china, and glassware, as well as painting supplies. Like Detroit’s L.B. King store, she created a one-stop shop for young women interested in exploring china painting and, later, art pottery.
Title page, Tried by Fire, 1886. / THF627720
Frackelton made a national name for herself in 1886 with the publication of Tried by Fire. It differed from other manuals for china painters in that it was written by a teacher for beginning students. Frackelton’s conversational style and advice on not expecting too much too soon appealed to readers and the book became a best seller, reprinted in two revised editions in 1892 and 1895. As a teacher, Frackelton had no equal in the world of art pottery. She advocated that both wealthy and poor women could enjoy the art of china painting: “Beauty is the birthright of the poor as well as the rich, and he lives best who most enjoys it.”
Color plate from Tried by Fire, 1886. / THF627772
Color plate from Tried by Fire, 1886. / THF627773
Color plate from Tried by Fire, 1886. / THF627775
Color plate from Tried by Fire, 1886. / THF627774
Pitcher, 1890–1910, decorated by an amateur china painter. Note that the botanical decoration on this pitcher is similar to the Tried by Fire color plates. / THF176879
Another major innovation was the development of a patented gas-fired kiln, first offered in the advertising section of Tried by Fire. By 1888 she was granted a second patent for a new and improved version.
Advertising section of Tried by Fire showing Frackelton’s portable gas kiln. / THF627793
By 1890 Frackelton was a well-known figure and was noted for displaying her work in international exhibits. In 1893 she won eight awards for her work in a competition held at Chicago’s World’s Columbian Exposition. Additionally, she became renowned for her work in a variety of ceramic media, especially for her blue and white salt-glazed stoneware. She also worked to create new and easier-to-use paints for decoration. She went so far as to organize the National League of Mineral Painters in 1892, an organization “aimed to foster a national school of ceramic art and provide a link between china painters throughout the country.”
By the late 1890s, Frackelton’s reputation was secure, as were her finances. In 1897 she divorced Richard Frackelton and moved to Chicago and spent much of her time lecturing and promoting ceramic art. She collaborated with several ceramic artists, including the now famous George Ohr, a unique artist who called himself “the mad potter of Biloxi.” Together, they created several highly unusual pieces, now in the collections of the Wisconsin Historical Society.
In her later years, Frackelton moved away from working in ceramics, preferring to return to painting and working as an illuminator of manuscripts. However, Frackelton’s promotion of the ceramic arts made her one of the most admired female artists in America in the first decade of the 20th century. Susan Frackelton was a remarkable figure in American ceramics, justifiably earning her status as one of the prominent figures in the decorative arts and certainly in broadening the role of women in American society.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford. Many thanks to Sophia Kloc for editorial preparation assistance with this post.
Illinois, Wisconsin, 20th century, 19th century, women's history, teachers and teaching, making, furnishings, entrepreneurship, education, decorative arts, ceramics, by Charles Sable, books, art
Sidney Houghton: The Later Commissions

Cover of Sidney Houghton Brochure. / THF121214
From Houghton’s reference images in the brochure, we can document many commissions that are lost as well as provide background for some that survive. This post centers on Houghton’s later work for the Fords, and my evaluation of why the relationship ended.
The Dearborn Country Club

Dearborn Country Club in 1925. / THF135797
Dearborn Country Club in 1927. /THF135798
According to Ford historian Ford Bryan in his book, Friends, Families & Forays: Scenes from the Life and Times of Henry Ford, the Dearborn Country Club was created for executives at the Ford Motor Company. By the middle of the 1920s, Ford’s operations were centered in Dearborn, with nearly all the company’s upper echelon working from the Ford Engineering Laboratory or the nearby Ford Rouge Plant. According to Ford Bryan, the idea came from Henry and Clara Ford to provide Dearborn with the same amenities as elite suburbs such as the Grosse Pointes or the northern suburbs. They also wanted their associates and friends to have the best that money could buy. The project was an incentive for Ford executives to remain in Dearborn, but proved to be unprofitable for the company. Further, when Henry Ford tried to impose his wishes against smoking and drinking, the membership essentially ignored him. Because of this, the Fords rarely visited the Club.
Architect Albert Kahn, who famously designed the Rouge Plant, was hired to design the clubhouse, seen above. The building was finished in the fall of 1925 and was designed in the “Old English” or Tudor style, popular in England in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Formal Dance at the Dearborn Country Club, 1931. / THF99871
Dearborn Country Club Chef at Banquet Table, 1931. / THF99875
Light's Golden Jubilee Ushers at the Dearborn Country Club, October 21, 1929. / THF294674
We know through documents that Sidney Houghton worked on the interiors. What we have in the way of documentation is a furnishings plan, but little else. Period photos, such as those above, show the elaborate beamed ceiling in the ballroom designed by Albert Kahn, and the elegant lighting and window treatments, likely provided by Houghton.
Henry Ford Hospital and Clara Ford Nurses Home

Henry Ford Hospital and Clara Ford Nurses Home, 1931. / THF127760
Clara Ford Nurses Home, 1931. / THF127754
Nurses in front of Clara Ford Nurses Home, 1926. / THF117484
One of Henry Ford’s great humanitarian efforts was in founding Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit. It was created in 1915 and in 1917 was turned over to the federal government during World War I for military use. By the middle of the 1920s, the hospital was considered the major medical center in Detroit. In 1925, Clara Ford organized the Henry Ford Hospital School of Nursing, and she funded the building housing it, the Clara Ford Nurses Home, on the hospital campus.
Living Room inside Clara Ford Nurses Home, 1925. / THF127777
Only one photograph of the original interior survives, showing the living room on the first floor. This is absolutely the work of Sidney Houghton, done in what he would call the Elizabethan or Tudor style. The walls are covered with heavy, inlaid panels and the furniture is heavily proportioned, with carved turnings. The wood of choice during this period was oak, which Houghton described as the “Age of Oak.” The upholstered furniture is likewise heavy and large in scale.
Houghton Brochure: A Tudor Interior. / THF121227b
Houghton Brochure, Furniture from the "Age of Oak." / THF121217a
The End of the Relationship
By 1925, Houghton’s commissions were at or nearing completion. After this date, there is an abrupt end to the correspondence between Houghton and the Fords. The only subsequent communications are a telegram from 1938, congratulating the Fords on their 50th wedding anniversary, and a letter dating to 1941, thanking Henry Ford II for his work on supplying aid for Britain during the second World War. While we have no documentation on how the relationship ended, we do have documentation of one artifact that may shed light on this period. In 1925, Houghton gave the Fords a sterling silver model galleon or ship. Perhaps this is a reference to Houghton’s love of sailing. It appears on the cover of the Houghton brochure at the top of this post.
Was this a peace offering from Houghton to the Fords? Or was it a token of generosity from Houghton, a great navigator, to the Fords? We will never know, but it is interesting to contemplate the implications of this extraordinary gift.
I hope you’ve enjoyed my journey through an unknown aspect of the Fords’ life. Researching and writing about Sidney Houghton has been a pleasure.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford. Many thanks to Sophia Kloc for editorial preparation assistance with this post.
Additional Readings:
- Sidney Houghton: The Fair Lane Rail Car and the Engineering Laboratory Offices
Table, Used as a Writing Desk by Mark Twain, 1830-1860 - Women Design: Peggy Ann Mack
- The Webster Dining Room Reimagined: An Informal Family Dinner
design, healthcare, Detroit, Michigan, Dearborn, Clara Ford, Henry Ford, Sidney Houghton, furnishings, decorative arts, by Charles Sable
Sidney Houghton: The Fair Lane Estate
In my last two blog posts (“The Enigmatic Sidney Houghton, Designer to Henry and Clara Ford,” and “Sidney Houghton: The Fair Lane Rail Car and the Engineering Laboratory Offices”), I discussed how Sidney Houghton (1872-1950), a British interior designer and interior architect met and befriended Henry Ford during World War I, and worked on projects like Henry Ford’s yacht Sialia, Henry and Clara Ford’s private railcar Fair Lane, and offices for Henry and Edsel Ford in the Ford Engineering Laboratory in Dearborn, Michigan. This blog centers on the most intimate of Houghton’s work for the Fords, the Fair Lane estate.
(For clarity’s sake, it is important to note that the Fair Lane estate is a historic house museum, independent of The Henry Ford. The house is currently undergoing a major restoration. You can learn more about the Fair Lane estate here.)
The Fair Lane Commission

Cover of Houghton Brochure / THF121214
The single document that best details the relationship between Sidney Houghton and the Fords is a brochure, more a portfolio of projects, published by Houghton in the early 1930s, to promote his design firm. From Houghton’s reference images, we can document many commissions that are lost as well as provide background for some that survive. Unfortunately for us, images of Fair Lane were not included in the 1930s Houghton brochure, likely because of the private nature of the commission.
However, The Henry Ford’s Benson Ford Research Center holds exterior and interior photographs of the house, taken at a variety of dates. Additionally, our archives holds a select group of Houghton’s designs for Fair Lane’s furniture. These are the only surviving drawings of Houghton’s Ford-related furniture. One of my greatest joys in researching this blog was locating the completed pieces of furniture in historic photographs.
The Story of Fair Lane
The story of Fair Lane began in 1909, when Henry Ford bought large tracts of land in Dearborn Township, the place of his birth. At that time, Henry, his wife, Clara, and their son, Edsel, were living comfortably in the fashionable Boston-Edison neighborhood of Detroit, not far from the Highland Park plant where the famous Model T automobiles were manufactured. Henry was considering options for building a larger home, where he and his family could have more space and greater privacy. They were also considering building in Grosse Pointe, a community where many of Detroit’s leaders of industry were constructing homes. They even bought a parcel of land there that eventually became the site of Edsel and his wife Eleanor’s home in the 1920s.
In the summer of 1909, Ford visited the renowned architect Frank Lloyd Wright in his Oak Park, Illinois, studio. The result was a commission for a large estate along the Rouge River in Dearborn. Scholars believe that Henry Ford heard about Wright from one of his chief engineers and neighbor, C. Harold Wills, who previously contracted Wright to build a home for his family in Detroit. By November of 1909, Wright had closed his studio and turned his practice over to the Chicago architectural firm of Von Holst and Fyfe, with his best draftsperson, Marion Mahony, overseeing all of Wright’s remaining projects. Wright felt that his architectural practice was at a “critical impasse” and went to Europe to work on a summary portfolio of his career, published in 1910. He was accompanied by Mrs. Mamah Borthwick Cheney, the wife of a client. This scandalous situation seems not to have affected the Fords, as Marion Mahony continued work on Fair Lane.
Presentation Drawing of Fair Lane, 1914 / THF157872
The project continued slowly through the next few years, until circumstances in the Fords’ lives made securing a new home a priority. In January 1914, Henry Ford announced his famous “five dollar day” wage for factory workers. His home on Edison Avenue near the plant was besieged by job seekers and the Fords lost any semblance of privacy. They soon realized that that the new Dearborn house was a priority. In February 1914, Clara Ford, who had taken the leadership role on the new house, called a meeting of Von Holst, Mahony and related designers. A number of elegant presentations of the home were shown to Clara Ford, including the design above. Many of these are now in public collections and give us a sense of the proposed estate. Two can be accessed here and here.
Instead of continuing to work with Marion Mahoney, Clara Ford chose Pittsburgh architect William Van Tine to complete the house. Van Tine was known in New York and the East, and it is generally thought that Clara Ford was seeking to emulate the tastes of women of her social status. Another key factor was the direction of American taste: the Prairie style promoted by Frank Lloyd Wright and Marion Mahony was rapidly losing currency and Americans increasingly favored revival styles, including Colonial and Medieval Revivals.
Fair Lane as Built

Fair Lane from the Rouge River, 1915 / THF98284
Fair Lane Entrance, 1916 / THF149961
When I look at images of Van Tine’s house, completed in early 1916, I am struck by the odd composition, such as the sloping horizontal rooflines, especially to the left of the front entrance. These seem derived from Marion Mahony’s designs. There are vertical, castle-like forms, such as the one just to the right of the entrance, which are not at peace with the rest of the house. The result is a hodge-podge of disharmonious elements that barely coexist with each other.
Planting Plan for Fair Lane Grounds Number 5, November 1915 / THF155894
The planting plan above gives us a sense of Van Tine’s arrangement of the house. To the far left is Henry Ford’s power house, which is connected to the house through a tunnel under the rose garden. The tunnel ends near the indoor swimming pool intended for son Edsel’s use.
Entry Hall from the Living Room around 1925 / THF126547
Library in 1951 / THF98258
Living Room in March 1916 / THF126073
The main rooms of the house are indicated in an area labeled as “residence” on the plan. The first-floor entrance consists of a grand hall and wide staircase. To the right of the hall is a small library. The hall leads into what the Fords described as their living room, the heart of the house. At the rear of the photograph above, please note the player organ installed in late 1915.
Music Room in 1951 / THF126543
The entrance to the music room is to the right of the player organ in the living room. It is by far the largest and grandest room in the house. The photograph above shows it in its final incarnation, shortly after Clara Ford’s death.
Dining Room in 1925 / THF98262
The dining room leads off the living room and is another grand room, although it lacks the scale of the music room. As you can see, all the large public rooms at Fair Lane are rather dark and heavily decorated.
Sun Porch, Identified as the Loggia on the Ground Plan, about 1925 / THF137033
The sun porch is unlike any other public room in Fair Lane. It was filled with light and was said to have been one of the Fords’ favorite rooms. Also, unlike the rest of the house, it was filled with wicker furniture.
As you can see, Fair Lane was a very dark and heavily decorated home. We know that the Fords—Clara in particular—were unhappy with the interior. For example, sometime in the 1920s or the 1930s, Clara Ford went so far as to paint the walnut paneling in the music room. This north facing room must have appeared very dark, especially on a cloudy winter day.
Sidney Houghton’s Work at Fair Lane
Records in the Benson Ford Research Center indicate that Sidney Houghton began consulting on furnishings for Fair Lane in 1919. The records and correspondence continue through 1925, with proposals and payments through the entire period. The only “before” and “after” photographs that we have are of the living room.
Living Room in 1919 / THF132991
Living Room in 1940 / THF136074
By 1940, the furnishings of 1919 have been completely removed. The clutter of the 1919 furnishings have been replaced with groups of furniture oriented around the fireplace. The whole arrangement appears coherent and logical. The furniture styles of the 1940 living room are a mixture of historic English and American. Is this the work of Sidney Houghton? While we know that Houghton was working extensively at Fair Lane, we have no surviving renderings for furniture in this room.
Houghton’s Documented Designs for Fair Lane

Master Bedroom in 1951 / THF149959
Like the living room, the master bedroom contains a mixture of furnishings in historic English and American styles. For example, the mantelpiece is described as a “Wedgewood,” as the colored decoration derives from Wedgewood’s English Jasperware, first made in the 18th century. There are also pieces that are American in origin, such as the William and Mary–style table in front of the fireplace, and the Federal-style slant front desk in the corner, to the right of the window.
This room also contains two twin beds, likely designed by Sidney Houghton. They are made of veneered walnut with inlaid medallions done in a Chinoiserie style, a western interpretation of oriental design.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Bed, 1921-1923 / THF626014
The headboard and footboard, as well as the crest rail and legs, of this bed are identical to those on the twin beds in the 1951 photograph. Houghton may have presented this design to Clara Ford, and she chose to have twin beds without a canopy produced instead.
Master Bedroom in 1951 / THF149955
The opposite wall in the master bedroom shows us again a combination of English and American historic furniture. They include an American Queen Anne oval table in the left corner. To the right of it is a Queen Anne style dressing table, partly obscured by an upholstered armchair. What is of interest is the dressing table and mirror at the center of the back wall. These are Houghton’s designs.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Bedroom Dressing Table and Looking Glass, 1921-1923 / THF626012
We can see that the dressing table matches the bed—the inlaid medallions are also done in a Chinoiserie style—so this appears be part of a bedroom suite. Indeed, there is another design that does not appear in the room.
Design by Sidney Houghton Design for Fair Lane, Bedroom Cabinet or Chest, 1921-1923 / THF626016
This piece likely was presented to Clara Ford and rejected, or, if produced, removed before the photograph was taken in 1951.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Chest of Drawers and Case, possibly for Bedroom, 1921-1923 / THF626010
This chest of drawers appears to relate to the bedroom suite, as it is similar in scale, although it lacks the inlaid medallions.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Ladies Writing Table, 1921-1923 / THF626008
This elegant ladies desk may have been intended for the Fords’ bedroom. Like the chest, it may have been rejected or removed later.
The Benson Ford Research Center holds more of Houghton’s furniture designs for Fair Lane, although none appear in the historic photographs.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Center Table or Partners Desk, 1921-1923 / THF626002
This heavy, masculine-looking piece was likely not part of the bedroom suite. If fabricated, it would have been a large, clunky piece of furniture.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Side Table, 1921-1923 / THF625998
This piece, done in the Louis XV or 18th-century Rococo style is a departure from anything visible at Fair Lane. Clara Ford likely rejected it.
There are also Houghton sketches and working drawings in the archive.
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Slant Front Desk and Chair, 1921-1923 / THF625994
Design by Sidney Houghton for Fair Lane, Side Table or Stool, 1921-1923 / THF626000
These designs were likely drawn on-site and presented as ideas for Clara’s approval.
Conclusion
As these drawings suggest, Sidney Houghton was extremely talented. He could work in a variety of styles and produced high-quality furniture. He transformed Fair Lane during the early 1920s from an eclectic mix to a more simplified combination of 18th-century English and American styles. This post represents the beginning of inquiry into the role of Houghton at Fair Lane, which should be continued over time. My next blog post will examine Sidney Houghton’s later work for the Fords and the end of their relationship.
Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford. Many thanks to Sophia Kloc, Office Administrator for Historical Resources at The Henry Ford, for editorial preparation assistance with this post.
Additional Readings:
- Armchair Made from Longhorn Steer Horns, 1904-1910
- Prototype Eames Fiberglass Chair, circa 1949
- Sidney Houghton: The Fair Lane Rail Car and the Engineering Laboratory Offices
- Creatives of Clay and Wood
20th century, 1920s, 1910s, Sidney Houghton, research, Michigan, home life, Henry Ford, furnishings, drawings, design, decorative arts, Dearborn, Clara Ford, by Charles Sable, archives

